Algorithmic Organizations: The Post-2025 Evolution
- Time ALGOR

- Aug 16, 2025
- 3 min read
Below is the timeline and cast of characters based on the sources provided:
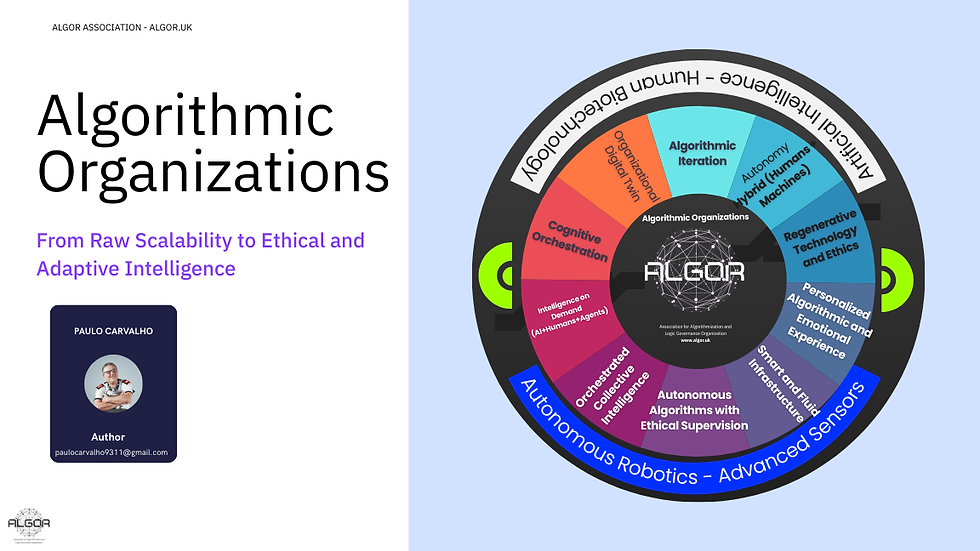
Detailed Timeline
2014: Release of the book "Exponential Organizations" by Salim Ismail et al., which defines the attributes for emerging companies to grow rapidly (e.g., real-time dashboards, on-demand staffing, algorithms). This book lays the foundation for the dominant organizational model before 2025.
Period Before 2025 (as of the current time of publication): On-Demand Staffing: Use of temporary teams and freelancers (e.g., Upwork, Fiverr) to reduce fixed costs and increase flexibility.
Community and Crowd: Crowdsourcing and open platforms (e.g., Wikipedia, Kickstarter) for collaboration and funding.Algorithms: Automation of repetitive decisions (e.g., email sorting, simple product recommendations). These algorithms were effective, but opaque and lacked ethical oversight.
Leveraged Assets: Business models that use third-party resources (e.g., Airbnb, Uber) to optimize costs and scale.Engagement: Focus on generic advertising campaigns, points programs, and simple gamification for mass engagement.Interface: Traditional graphical application interfaces with rigid menus and manual field filling.Dashboard: Real-time dashboards to monitor metrics and KPIs, but with little predictive or simulation capability.Experimentation: Agile testing and continuous MVPs in small groups of users, with manual human feedback.Autonomy: Autonomous teams with operational decision-making power (e.g., Spotify squads), but still within an exclusively human logic.Social Technology: Digital platforms (e.g., Facebook, Twitter) that connected people en masse, prioritizing engagement, but generating side effects such as misinformation.2025 (and beyond): The world changes radically; artificial intelligence gains agency, and algorithms make autonomous decisions. Human interaction occurs with hybrid networks of sensors, robots, digital twins, and personal biotechnology.
Staff on Demand → Intelligence on Demand (AI+Humans+Agents): The workforce becomes hybrid and orchestrated by intelligent systems (e.g., LangChain, custom GPTs, Deel, Toptal, Humata, Vocode, AutoGPT). The emphasis is on the dynamic reorganization of the cognitive ecosystem.Community and Crowd → Orchestrated Collective Intelligence: Communities transform into autonomous, intelligent networks guided by algorithms, with automated incentives and decentralized validation (e.g., DAOs like Uniswap, Aragon, SingularityNET).
Algorithms → Autonomous Algorithms with Ethical Oversight: Algorithms learn, decide, and evolve under ethical frameworks, explainability, audits, and governance (e.g., ISO/IEC 42001, AI Act, PL 2338/23). Companies like OpenAI, Anthropic, and IBM watsonx.governance implement ethical alignment and traceability systems.Leveraged Assets → Intelligent and Fluid Infrastructure: Physical and digital assets are sensorized, connected, interoperable, and managed by AI in real time (e.g., Amazon Smart Warehouses, Prologis, Bosch and BMW smart factories).
Engagement → Personalized Algorithmic and Emotional Experience: User relationships are curated by AI, emotionally adjusted through biometric data, and delivered in real time (e.g., TikTok, Replika AI, Nike, Spotify, Zendesk AI).Interface → Cognitive Orchestration: Cognitive orchestration systems with generative AI adapt the user experience, personalize interactions, and make decisions based on sensory data and context (e.g., IBM watsonx Assistant, Salesforce Einstein, ChatGPT, NuBank with generative AI).
Dashboard → Cognitive Twin (Organizational Digital Twin): Organizations use digital twins, living algorithmic models that simulate and project the future (e.g., Microsoft Azure Digital Twins, Siemens Xcelerator, Dassault Systèmes 3D EXPERIENCE, Ansys Twin Builder).Experimentation → Algorithmic Iteration: AI models and digital simulations are used to test and evolve products before launch, with feedback loops from sensors and biobehavioral data (e.g., Amazon, Netflix, Waymo, Meta AI).Autonomy → Hybrid Autonomy (Humans + Machines): Autonomy is distributed among humans, autonomous AI agents, and robots, requiring coordination protocols and ethical oversight (e.g., Amazon Fulfillment Centers, Tesla Gigafactories, smart hospitals in South Korea).
Social Technology → Regenerative and Ethical Technology: The focus is on creating technologies that regenerate social bonds, respect privacy, and promote human well-being (e.g., BeReal, Humanetech.com, Claude (Anthropic), Apple, Khan Academy with AI tutor).Cast of Characters
Paulo Carvalho: Author of the material "Algorithmic Organizations: From Raw Scalability to Ethical and Adaptive Intelligence." He is responsible for this critical reinterpretation of the "Exponential Organizations" model in light of the radical changes post-2025.
Salim Ismail et al.: Authors of the classic book "Exponential Organizations" (2014), which defined the attributes for the rapid growth of emerging companies. Although not an active character in the 2025 context, his work is the starting point and reference for the update proposed by Paulo Carvalho.
ALGOR (Association for Algorithmization and Logic Governance Organization): A professional membership organization with a registered domain in the United Kingdom (London) and legal representation in Brazil through XPER BRAZIL MANAGEMENT IN TECHNOLOGICAL INNOVATION LTDA. It is the entity that publishes the material, advocating an ethical and adaptive approach for organizations in the era of AI and autonomous algorithms.
XPER BRAZIL MANAGEMENT IN TECHNOLOGICAL INNOVATION LTDA: The legal entity representing ALGOR in Brazil. Its address and contact information are provided, indicating its operational and management role for ALGOR in the country.




Comments